The essentials of social cohesion: A literature review
Key facts
Identity/feeling of belonging
Participation
Orientation towards the common good
Tolerance
Connectedness
Other (Other)
Vertical dimension (between individuals or groups and institutions)
Overview
Social cohesion is “a descriptive attribute of a collective, indicating the quality of collective togetherness”.
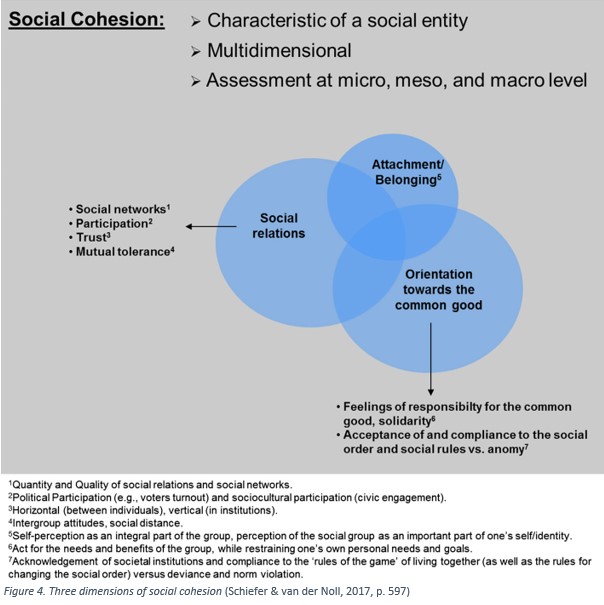
Based on a comprehensive review of the literature, Schiefer and van der Noll (2017) identify three essential dimensions of social cohesion (Fig. 4). Firstly, socially cohesive societies are characterized by close social relations, e.g. through strong social networks, high levels of institutional and social trust and civic participation in public life. Secondly, members of society feel emotionally connected to the social entity, i.e. the social group is an important part of their identity. Thirdly, an orientation towards the common good prevails, i.e., citizens feel responsible for the welfare of society, they embrace solidarity and comply with the social order.
By focusing on these three dimensions, Schiefer & Noll advocate a ‘slim’ concept of social cohesion that is distinct from related concepts such as inequality, well-being, and shared values. A slim conceptualization is useful as it allows to differentiate between core components, causes, and consequences of social cohesion. For instance, inequality can be analyzed as potential driver of social cohesion and well-being as a consequence of cohesive societies.