Back to Results
Is it ethnic fractionalization or social exclusion, which affects social cohesion?
Key facts
Journal/Publisher
Social Indicators Research
Type of publication
Journal article
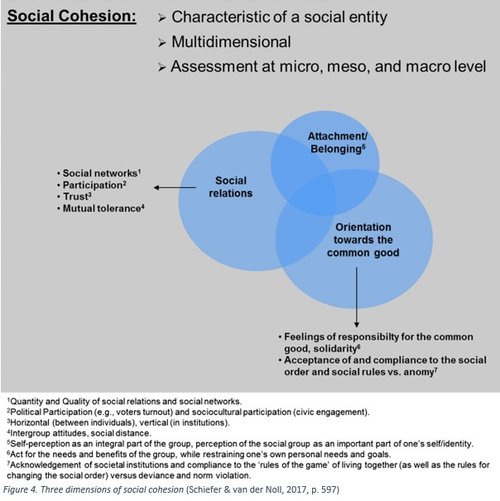
Elements of social cohesion
Intergroup relations
Equality/Inequality
Connectedness
Equality/Inequality
Connectedness
Geographical focus
Empirical
Main thematic areas
Economic development
Inequality
Inequality
Summary
The theory about missing links of economic growth often lags behind the empirical estimations of such links. A consensus has emerged that ethnic fractionalization has a negative impact on growth, also when controlled for income inequality. Often, although implicitly, the assumed channel is social cohesion. We analyse the effect of fractionalization on social cohesion with a different inequality measure, namely a social measure of inequality: the Inclusion of Minorities Index. Our results indicate that it is social exclusion, which reduces social cohesion, rather than diversity as such. We conclude that future studies of social cohesion and its relation to growth may benefit from using measures of social exclusion next to ethnic diversity.

Download