The Historical Roots of Well-Being and Social Cohesion
Key facts
Other (Education)
Summary
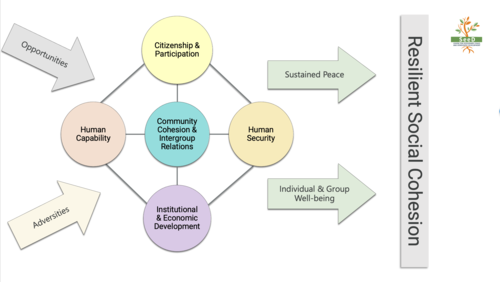
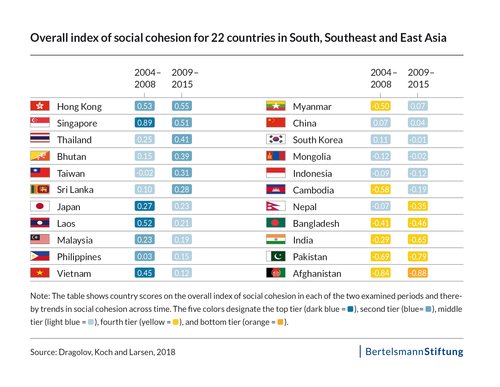
A country’s levels of well-being and social cohesion are largely stable over long periods of time. Two key determinants of well-being—equality and education—follow this ‘path dependence’. This paper reviews these relationships and then move to a discussion of how early levels of education influence contemporary well-being. It finds that education matters for social cohesion, and that historical levels of education are mostly more important than contemporary enrollments. The evidence largely comes from the West because of data availability, but there is support for this claim in other regions. There is also evidence that countries can catch up, as the case of many East Asian nations shows. Yet change is not easy given the ‘stickiness’ of inequality and the high correlation between mean school years in 1870 and 2010. It is difficult to organize poor (and uneducated) citizens, and to ensure a country’s leaders will provide resources for the poor. Many countries do not have sufficient economic or other resources or the political support to enact policies to change the distribution of human capital.