Social Cohesion Revisited
Key facts
Identity/feeling of belonging
Participation
Solidarity
Shared values
Tolerance
Other ()
Overview
Social cohesion is the “ongoing process of developing well-being, sense of belonging, and voluntary social participation of the members of society, while developing communities that tolerate and promote a multiplicity of values and cultures, and granting at the same time equal rights and opportunities in society”.
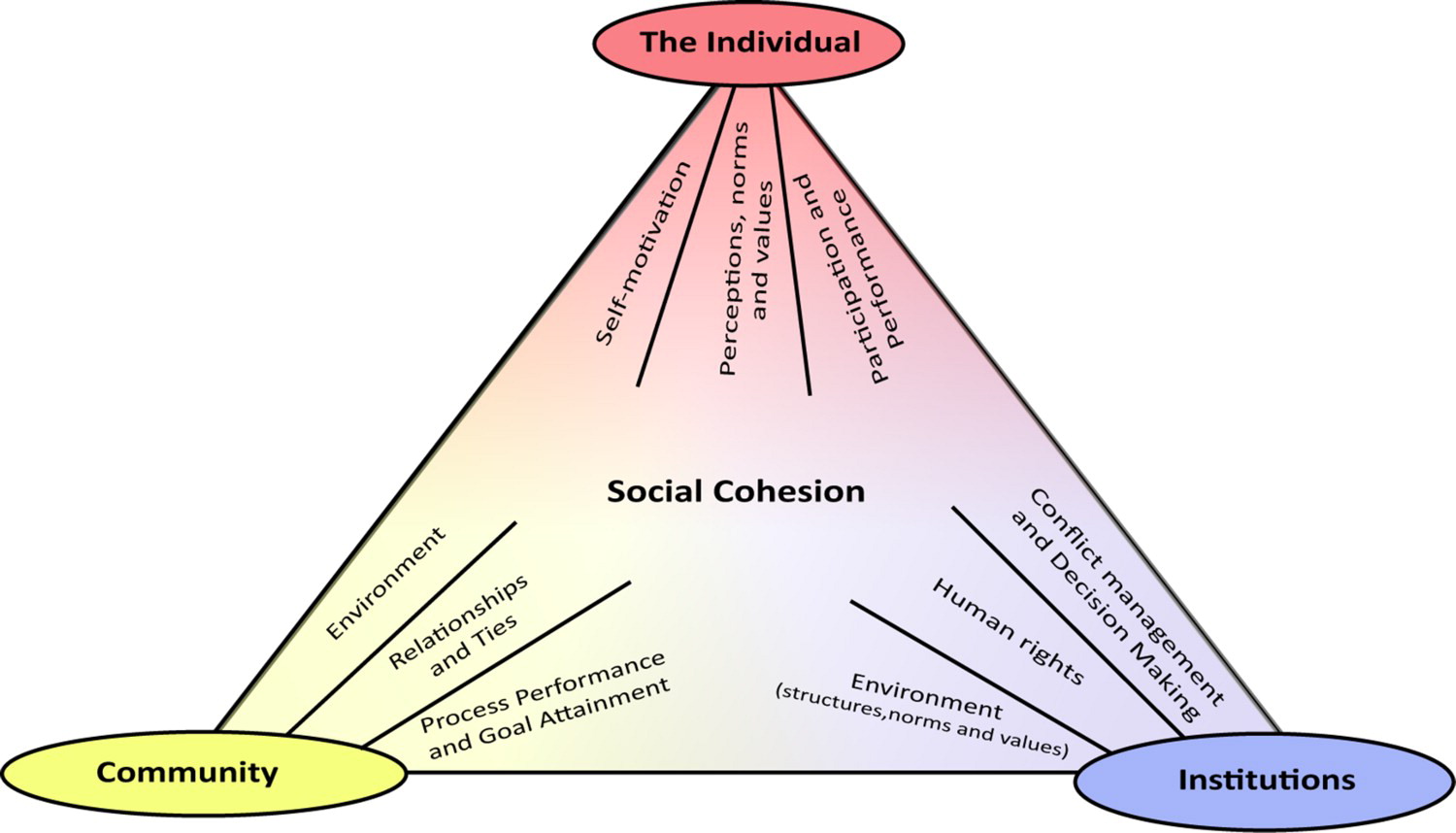
Fonseca et al. (2019) propose a three-level framework consisting of individual, community, and institutional aspects of social cohesion (see figure below).
At the level of the individual, social cohesion involves individuals’ motivation to belong to, participate in, and actively contribute to society and their sense of belonging to the social entity.
Social cohesion at the level of the community encompasses three key features: a social environment that is characterized by e.g. shared values, conformity, friendship networks, and civic engagement; communal relationships and ties, that manifest in e.g. social capital, trust, and solidarity; and the performance of communities in pursuing common goals and objectives.
At the institutional level, social cohesion incorporates institutional conflict management and decision making, e.g. through efforts to reduce inequalities and exclusion in society, as well as formal bodies that structure and uphold societal rules. Moreover, social cohesion manifests in institutional efforts to defend human rights and granting all citizens agency and freedom.
All three levels are interconnected. For example, individual participation and feeling of belonging to society require institutional structures that avoid exclusion, inequality, and marginalization.